Nature tourism
Cola del Embalse de Bornos natural area
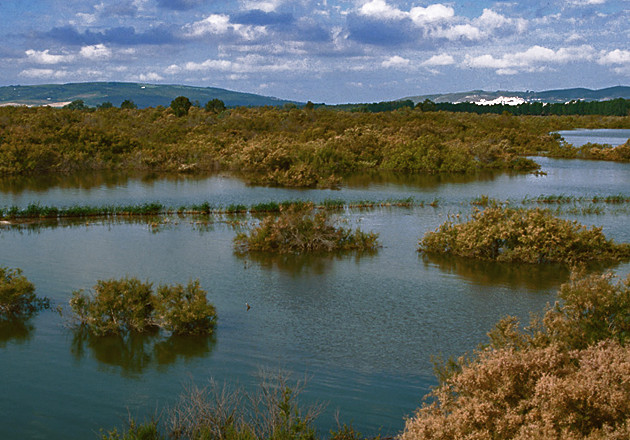
The tail of the Bornos Reservoir, located on the Guadalete river, in the north of the province of Cádiz, was officially declared a "natural area" in 1989. Law 2/1989, of July 18, of the Junta de Andalucía established the figure of protection of this extended environment between the populations of Bornos and Villamartín. It is a flood zone. When the dammed water level rises, all this land is flooded.
It is also an area that stands out for the faunal nesting practice, especially waterfowl, to which the existing formation of tamarisks contributes. It should be noted that this is the habitat of the otter, the osprey, the purple heron and the night heron.
The Cola del Embalse de Bornos Natural Area is located in the recoil of the reservoir on the Guadalete river from which it receives its name, in the municipalities of Bornos, Arcos de la Frontera and Villamartín, in the province of Cádiz. It has an area of 817 hectares. It was declared a Natural Site by Law 2/1989, of July 18, which approves the inventory of Protected Natural Areas of Andalusia and establishes additional measures for their protection (BOJA no. 60, of 07/27/1989 ); It is also a Special Protection Area for Birds [ZEPA (2002)], and is proposed as a Place of Community Interest (SCI).
It represents a nesting and wintering area for numerous protected bird species, with an important colony of Ardeids.
Among the species of birds that can be observed are the Night Heron (Nicticorax nicticorax), the Squacco Heron (Ardeola ralloides), the Little Egret (Egretta garcetta), the Purple Heron (Ardea purpurea), the Stilt (Himantopus himantopus), the Avocet ( Recurvirostra avosetta), the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo), the Gray Heron (Ardea cinerea), the Wigeon (Anas penelope), the Common Teal (Anas crecca), the Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos), the Shoveler (Anas clypeata ), the Eurasian Scotch (Melanitta nigra), the Moorhen (Gallinula chloropus), the Eurasian Coot (Fulica atra), the Northern Lapwing (Vanellus vanellus) and the Common Sandpiper (Calidris alpina). As far as ichthyofauna is concerned, there is the Vogue (Chondrostoma polylepis) and the Colmilleja (Cobitis taenia). Among the mammals is the Otter (Lutra lutra).
Among the reptiles is the Leprous Terrapin (Mauremys leprosa) and among the amphibians the Iberian Painted Frog (Discoglossus galganoi).